The Service Strategy phase enables the organization to ensure that the organizational objectives for IT are defined and that Services and Service Portfolios are maximized for value. Other benefits delivered include:
- Enhanced ability to predict the resources required to fund IT
- Clearer visibility of the costs for providing IT Services
- Quality information to support investment decisions in IT
- Understanding of the use and demand for IT Services, with the ability to influence positive and cost-effective use of IT.
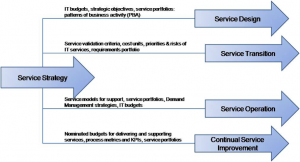
As the focal point for strategy, policy and guidelines that direct the efforts and practices of the IT organization, Service Strategy has many important interfaces with the rest of the Service Lifecycle. Some of these include:
- Interfaces with the Service Design phase:
- Service Archetypes and Models, which describe how service assets interact with customer assets. These are important high-level inputs that guide the design of services
- Definition of business outcomes to be supported by services
- Understanding of varying priority in required service attributes
- Relative design constraints for the service (e.g. budget, contractual terms and conditions, copyrights, utility, warranty, resources, standards and regulations etc.)
- Definition of the cost models associated with providing services.
- Interfaces with the Service Transition phase:
- Service Transition provides evaluations of the costs and risks involved with introducing and modifying services. It also provides assistance in determining the relative options or paths for changing strategic positions or entering market spaces
- Request for Changes may be utilized to affect changes to strategic positions
- Planning of the required resources and evaluation whether the change can be implemented fast enough to support the strategy
- Control and recording of service assets is maintained by Service Asset and Configuration Management.
- Interfaces with the Service Operation phase:
- Service Operation will deploy service assets in patterns that most effectively deliver the required utility and warranty in each segment across the Service Catalog.
- Deployment of shared assets that provide multiple levels of redundancy, support a defined level of warranty and build economies of scale.
- Service Strategy must clearly define the warranty factors that must be supported by Service Operation, with attributes of reliability, maintainability, redundancy and overall experience of availability.
- Interfaces with the Continual Service Improvement phase:
- Continual Service Improvement (CSI) will provide the coordination and analysis of the quality, performance and customer satisfaction of the IT organization, including the processes utilized and services provided.
- Integration with CSI will also provide the identification of potential improvement actions that can be made to elements of Service Strategy.