- Will the SLA structure allow flexibility in the levels of service to be delivered for various customers?
- Will the SLA structure require much duplication of effort?
- Who will sign the SLAs?
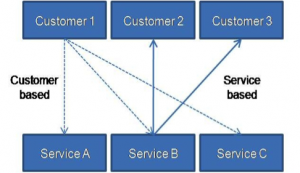
Three types of SLAs structures that are discussed within ITIL® are service-based, customer-based and multi-level or hierarchical SLAs.
Figure 5.D – SLA structures
Many different factors will need to be considered when deciding which SLA structure is most appropriate for an organization to use.
Typical Multi-level SLA Structure components:
- 1. Corporate level: All generic issues are covered, which are the same for the entire organization.
Example: The Corporate Security Baseline, e.g. Passwords, ID cards etc.
- 2. Customer level: Those issues specific to a customer can be dealt with.
Example: Security requirements of one or more departments within the organization are higher e.g. the financial department needs higher security measures.
- 3. Service Level: All issues relevant to a specific service (in relation to customer) can be covered.
Example: The email services for a particular department needs encryption and secure backups.
Using a multi-level structure for a large organization reduces the duplication of effort while still providing customization for customers and services (by inheritance).
You focus on defining the goals of your organization’s successful Service Level Management and let this toolkit guide you to the end result. |